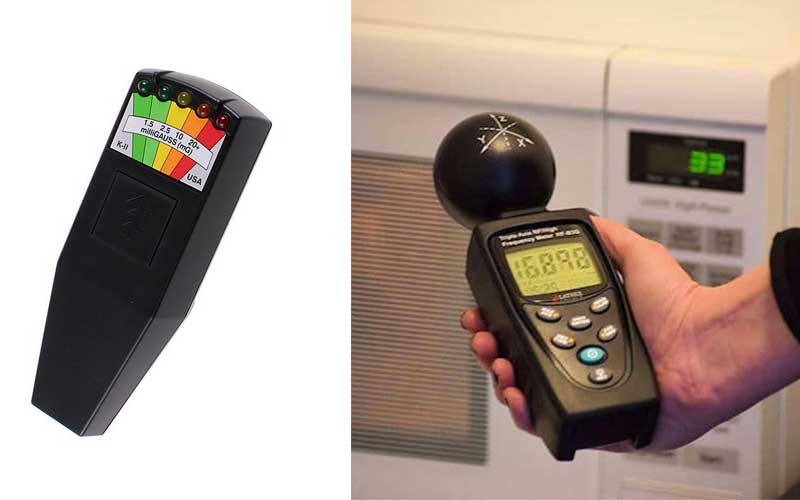
Electromagnetic field meters, also known as the EMF meters, are one of the most popular tools that are very essential at your workstation, or even at your own home.
This handy tool is used for measuring electromagnetic radiation flux density or basically the difference in the electromagnetic field over time.
Sounds complicated?
It can certainly be complex but here’s a very brief explanation of what an EMF is.
The EMF can be generated by DC or AC currents.
AC electromagnetic fields can be measured using an EMF meter.
The said magnetic fields are typically emitted from man-made sources including electrical wiring, and many more.
If you are interested in more information about how the EMF meter works, then you’ve come to the right article.
This article will not only provide you details on how an EMF meter measures radiation, but it will also tell you its applications and vouch for some examples of the outstanding products available in the market.
So, what are you waiting for?
Let’s scroll down!

About Electromagnetic Fields
To start with, electromagnetic fields are present in our environment and even in sources that are human-made.
One of the electromagnetic fields that naturally occurs in our environment is electrical charges that come from thunderstorms and even our own planet’s electromagnetic field.
On the other hand, TV antennas, X-Rays, electrical appliances, and electrical wires are some of the well-known man-made or industrial sources.
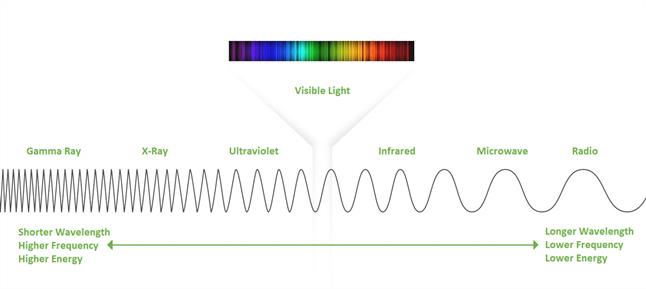
Electromagnetic fields are known to have different wavelengths and frequencies.
Wavelengths are indirectly proportional to frequencies.
This means that when there is a high frequency, the wavelength is shorter, and when there is a low frequency, the wavelengths are much greater.
Moreover, electromagnetic fields are generated by both the AC and DC currents.
These are the combination of magnetic energy and electric energy.
Stationary charges, which generate electromagnetic fields only in the surrounding spaces, are measured in volts per meter (V/m).
Meanwhile, the magnetic field that is generated by moving charges, like currents, creates flux densities that are measured in MilliTesla (mT) or MicroTesla (µT).
Types of EMF Meters and What They Measure
Electromagnetic meters or EMF meters can measure both DC electromagnetic fields or AC electromagnetic fields which are sometimes called Magnetometers or a Gauss Meter.
EMF meters can be used in many different ways. These meters are used to test appliances in buildings, or even in your own humble abode.
They are also used to check the electromagnetic field that is emitted from power lines and detect other troubleshooting applications if there are any.
There are two main types of Electromagnetic meters, namely the single-axis meters and the tri-axis meters.
The single-axis meters allow you to measure one dimension on the field.
In order to obtain a full-field measurement, you have to turn and tilt these meters.
In comparison to tri-axis meters, single-axis meters are much less expensive.
Tri-axis meters, on the other hand, allow you to obtain much faster results because it measures tree axes at one go.
They say time is one thing money can’t buy.
Hence, this is the reason why tri-axis meters are more expensive than single-axis meters because it doesn’t only make your measurements quicker, it also saves you money because time is gold.
Product Examples
There are many kinds of EMF meters, both in single-axis and tri-axis categories.
Here are a couple of examples to help you know more and understand the different variations of EMF meters, as well as their different specifications and features.
Single Axis Meter
Handheld EMF Radiation Tester


Product Code: EMF -823
The EMF-823 is a handy and reliable EMF radiation tester.
The said product allows you to quickly determine the EMF levels around industrial services, home appliances, and power lines.
The EMF-823 does not only provide an EMF result in as little as 0.4 seconds, it’s also very simple and easy to use.
Quick Specifications of the EMF-823 are the following:
- Measurement Units: microtesla, milligauss
- Accuracy:
- ± (10 % + 5 d) – 2,000 microtesla/20,000 milligauss range. * Spec. accuracy tested under 50 Hz or 60 Hz
- ± (5 % + 3 d) – 200 microtesla/2,000 milligauss range.
- ± (4 % + 3 d) – 20 microtesla/200 milligauss range.
- Range Tesla:
- 2,000 microtesla x 1 microtesla
- 200 microtesla x 0.1 microtesla
- 20 microtesla x 0.01 microtesla
- Range Gauss:
- 20,000 milligauss x 10 milligauss
- 2,000 milligauss x 1 milligauss
- 200 milligauss x 0.1 milligauss
- Size and weight: 163mm x 68mm x 24mm, 215 grams.
- Measurement Axis: Single Axis
Tri-Axis Meter
3 Axis Handheld Electromagnetic Field (EMF) Tester


Product Code: EMF-828
The EMF-828 is a handheld and accurate EMF tester.
The said tool has a separate probe that aids a simple remote operation.
This EMF tester also makes use of a three-axis EMF measurement to identify the radiation levels around TV sets, power lines, video machinery, computer monitors, and other similar industrial devices.
Listed below are the quick specifications of the EMF-828:
- Measurement Units: microtesla and milligauss
- Accuracy:
- ± (10 % + 5 d) at 2,000 microtesla/20,000 milligauss range
- ± (5 % + 3 d) at 200 microtesla/2,000 milligauss range.
- ± (4 % + 3 d) at 20 microtesla/200 milligauss range.
- Range Tesla:
- 2,000 microtesla x 1 microtesla
- 200 microtesla x 0.1 microtesla
- 20 micro Tesla x 0.01 microtesla
- Range Gauss:
- 20,000 milligauss x 10 milligauss
- 2,000 milligauss x 1 milligauss
- 200 milligauss x 0.1 milligauss
- Size and weight: 237 x 60 x 60mm, 200 grams
- Measurement Axis: Tri-Axi
